Home > Tree biology > Cork cambium
Tree biology
Contents: - periderm - phellem - cork cambium - phelloderm - cortex - phloem- phloem rays - sieve tube element - companion cells - cambial zone (cambium) - bark - xylem - growth ring - vessels - tyloses - parenchyma - axial parenchyma - multiserrate ray parenchyma - uniserrate ray parenchyma - fibers - symplast - apoplast - growth ring/ray compartment - wounding response - decay development
Select any of the above terms to view its location in the tree cross section. Text at bottom.
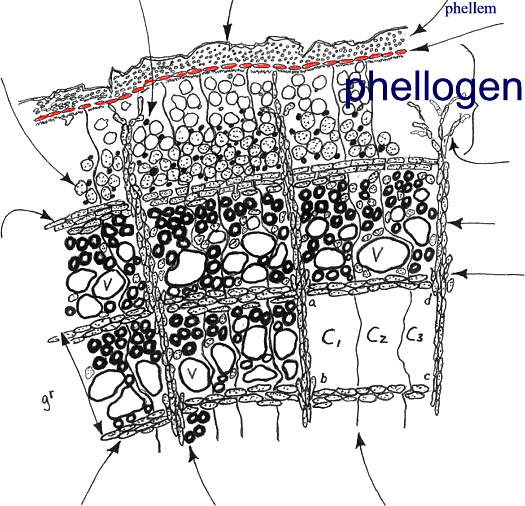
Phellogen
layer or cork cambium is a dividing zone of cells that forms phellem to
the outside and phelloderm to the inside. In other words, it forms the
outer bark. This cambial zone is constantly on the move outward as the
tree grows. New phellogens can form deeper within the phloem and push
the older phellogen with its phellem outward. Chlorophyll can be found
in and around the phellogen.

