Home > Tree biology > Compannion cells
Tree biology
Contents: - periderm - phellem - cork cambium - phelloderm - cortex - phloem- phloem rays - sieve tube element - companion cells - cambial zone (cambium) - bark - xylem - growth ring - vessels - tyloses - parenchyma - axial parenchyma - multiserrate ray parenchyma - uniserrate ray parenchyma - fibers - symplast - apoplast - growth ring/ray compartment - wounding response - decay development
Select any of the above terms to view its location in the tree cross section. Text at bottom.
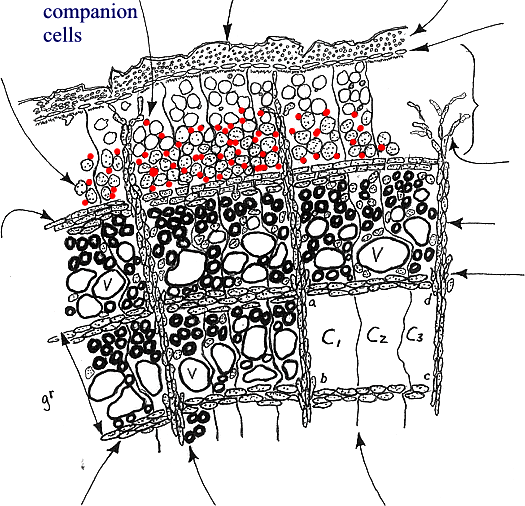
Companion
cells are alive and contain a nucleus. They are located adjacent to sieve
tube elements which do not contain a nucleus. Companion cells help the
sieve tubes function in moving sugars from leaves toward roots.

